To assist shed some mild on the subject of English phrase stress guidelines, I not too long ago interviewed English pronunciation coach Jennie Reed. Jennie is an skilled English instructor from southern England.
Earlier than introducing Jennie, I’ll briefly introduce the subject of English phrase stress. After sharing a brief biography of Jennie, I’ll share the interview. Then, I’ll go into a few of the guidelines of English phrase stress, ably assisted by some glorious articles and books I’ve learn. I shall spherical issues off with certainly one of Jennie’s workouts on phrase stress, adopted by some closing ideas.
An Introduction to English phrase stress
In a nutshell, phrase stress is the time period used to explain the emphasis or accent given to a selected phrase when announcing it. Except for ‘emphasis’ and ‘accent’, stress may additionally be known as ‘prominence’ (Rogerson-Revell, 2011, p.137). In English phrases which comprise a couple of syllable, we don’t often pronounce every syllable with the identical weight. Due to this fact, syllables in a phrase could both be careworn or unstressed.
Longer English phrases could have a couple of careworn syllable. Nonetheless, certainly one of them tends to be emphasised greater than the opposite(s). That is the place main and secondary stress come into play. The syllable with the first stress connected to it clearly stands out probably the most.
Other than main and secondary stress, it’s additionally value mentioning unstressed syllables. In English, virtually all unstressed syllables have schwa [ə] for his or her vowel, although [i] can even typically be unstressed, just like the [i] in nippy [/ˈnɪp.i/]. Proficient audio system of English are inclined to shorten the unstressed syllables a lot that the vowel sound virtually solely disappears.
On this put up, I method the subject of English phrase stress guidelines with some warning. Oftentimes, on the subject of language studying, there aren’t any laborious and quick guidelines. Certainly, as Kelly (2000, p.68) and Underhill (2005, p.55) argue, it’s extra acceptable to explain phrase stress by way of “tendencies” versus guidelines. Extra to come back on these tendencies all through this put up.
All about Jennie Reed
Initially from Essex, England, Jennie now lives in Alloa, Scotland.
Quickly after graduating in German and Italian, Jennie obtained her TEFL certificates with the Worldwide TEFL Academy in 2010. A few of her first assignments in TEFL included a two-and-a-half-year stint educating English in Italy, a ten-month place educating English in Munich and a stretch educating worldwide college students in Chester, UK. Jennie subsequently labored as a instructor of English, Interim advertising supervisor and Interim Director of Research at Conlan College Ltd, additionally in Chester.
Between June 2016 and July 2020, Jennie labored as an English instructor at British Examine Centres in Edinburgh. Throughout that time period, she accomplished The Diploma in Educating English to Audio system of Different Languages (DipTESOL).
In August 2020, on the peak of the pandemic, Jennie turned her consideration to freelance tutoring on-line. That’s when she arrange Excellence in English Training. Basically, Jennie is targeted on serving to college students to develop their pronunciation expertise. She additionally helps passionate English Academics ship inspiring and interesting classes in order that they’ll create optimistic, long-lasting adjustments within the classroom.
Today, Jennie additionally volunteers as an ESL instructor for the non-profit organisation RefuAid. RefuAid assists refugees and asylum seekers all around the UK to entry larger training, requalification and employment.
Interview – English phrase stress guidelines with Jennie Reed
1. Relating to English phrase stress guidelines, there are fairly blended emotions within the literature. Dauer [2005, p.548] argues in favour, stating that “college students have to be taught phrase stress as a result of it doesn’t seem within the writing system and lots of aren’t conscious of its significance.” In reality, Dauer [2005] takes one other author Jenkins [2000, in Dauer, 2005] to process. Jenkins believes that phrase stress is unteachable, unlearnable, and pointless from the angle of a non-native speaker. Dauer fights again, giving the instance of polysyllabic phrases. Based on Dauer [2005, p.547], a handful of primary guidelines can account for 85% of polysyllabic phrases [see Dauer, 1993, pp.67-68].
With Dauer at one finish of the spectrum, and Jenkins on the different, the place do you stand on the controversy surrounding the teachability of phrase stress?
I believe it may be useful for some college students to grasp English phrase stress guidelines. Some college students want the foundations to have the ability to apply them and use them effectively. For different college students, it’s not so necessary. They’re extra interested by utilizing the language as they discover it. It’s very a lot student-dependent.
From a pupil’s perspective, it’s not essentially a nasty factor to know the foundations. Generally, simply having one or two of the foundations might be useful. Nevertheless, it’s necessary to keep in mind that there are all the time exceptions to a lot of the guidelines we have now.
After we stress a sure syllable in a phrase, it’s all the time the vowel that’s careworn – by no means the consonants. I by no means even realised that phrase stress labored like this till I started to seek out my ft as a instructor.
2. Simply extending query 1 just a little. Adrian Underhill shoots straight down the center in his e book Sound Foundations: Studying and Educating Pronunciation. Underhill [2005, p.55] emphasises that “Some guidelines are advanced to use, and even then have many exceptions. In reality, tendency could also be a greater time period than rule.”
Underhill went on to notice that “the most effective rule is to be alert, to note what you might be doing and what the language is doing, and to replicate.” So, related to such noticing and reflection, Underhill [ibid.] believes academics can foster the event of learners’ “intuitive studying colleges in order that underlying tendencies can emerge inside every learner with out essentially having to be described or defined”. Do you suppose low-level learners actually have the capability to resort to such “intuitive studying colleges”?
I imagine that except college students are given some steering and really requested to note particular issues, it may be actually troublesome for college students to consider phrase stress. It is because they’ve so many different issues to think about, from lexical choice proper by means of to whether or not they’ve obtained the grammar proper. Frankly, I believe phrase stress is without doubt one of the final issues that they give thought to.
My argument stays the identical as in my reply to your first query. From a instructor’s perspective, I do suppose that it’s value specializing in phrase stress with a selected pupil if it is going to be useful for them.
3. I’ve had a tough time educating phrase stress to Polish learners of English as phrase stress falls on the penultimate syllable of their mom tongue? Are you able to describe your expertise with imparting English phrase stress guidelines to learners of first languages the place accent or phrase stress is mounted?
Most of my expertise not too long ago has been with Italian college students. Like Polish phrases, Italian phrases even have a really mounted phrase stress. Certainly, stress is positioned on the second final syllable in the vast majority of Italian phrases.
For Italians studying English, it’s much more necessary to spotlight the truth that there might be variations on the subject of English phrase stress. For instance, we stress two-syllable English phrases that may be each a noun and a verb otherwise; nouns on the primary syllable and verbs on the second syllable.
It’s necessary to show English phrase stress guidelines to Italians, for instance, in any other case they’d are inclined to pronounce each phrase the identical means. With two-syllable nouns and verbs, Italians often stress the primary syllable for each phrase lessons, except an accent is current on the ultimate syllable. I’m unsure that this causes confusion or miscommunication however it may make communication that bit slower in the event that they’re coping with native audio system. That’s in all probability why folks utilizing English at a excessive degree want to pay attention to English phrase stress guidelines. The Italian folks I’m working with are primarily academics of English. Due to this fact, it’s necessary for them to have the ability to perceive phrase stress tendencies to allow them to put the idea into observe within the classroom.
4. Are you able to speak just a little bit about the way you method educating the very advanced stress placement guidelines for various grammatical classes of a phrase, equivalent to two-syllable nouns and verbs in addition to compound nouns?
I believe any method to educating such stress guidelines ought to revolve round listening and repetition fairly than taking a look at any particular person phrases. As you talked about earlier, we don’t have any means of recognising phrase stress in written English.
Many of the phrase stress workouts I do are primarily based on listening and getting college students to take a look at phrases and mark the place they hear the stress. This will take fairly a little bit of observe but it surely’s rather more efficient than simply studying the phrases. In any case, they’re not going to see phrase stress highlighted with capital letters or daring script after they’re studying materials. Due to this fact, for me, the sensible facet of studying phrase stress is extra necessary.
5. How troublesome is it to show phrase stress on the subject of longer phrases, for instance, these with three, 4 and 5 syllables? Do you get entangled a lot with mentioning the place main and secondary stress happen in a given phrase?
I do contact upon the difficulty with my larger degree learners. It’s primarily in order that they’re conscious of it as a result of phrase stress is closely linked with sentence stress. As we don’t have mounted stress patterns which rely upon the variety of syllables, it’s extra necessary to be taught the perform of a phrase or the ending of a phrase. For instance, when phrases finish in -sion, -logy or -graphy – plus many extra endings – the earlier syllable is careworn: compreHEnsion, psyCHOlogy or phoTOgraphy.
So I don’t are inclined to ask my college students to be taught these so-called English phrase stress guidelines off by coronary heart. It’s extra about grouping some phrases collectively and simply getting them to hearken to the phrases and repeat the phrases.
Total, if college students get the stress within the incorrect place with longer phrases, it’s not more likely to trigger an enormous breakdown in communication.
6. We regularly discuss a bunch of phrases in English which have two stress patterns – that’s ‘robust’ and ‘weak’ kinds. Many of those phrases are perform phrases, equivalent to prepositions and pronouns. The overwhelming majority of the weak kinds are characterised by the diminished schwa vowel /ə/ for instance, a /ə/ e book – not a /ei/ e book. The place do weak kinds rank by way of significance in your pronunciation programs?
The schwa is the one phonemic image I insist all of my college students know. Having the ability to cut back that sound while you’re talking can improve your communication and comprehensibility of your spoken language.
Schwa positively contributes to fluency in that, inside sentence stress, you want each careworn and unstressed phrases working in good concord with each other. Schwa is important on the subject of sustaining a daily rhythm within the language.
I’d like so as to add that I believe it’s extra necessary to be taught chunks of language than it’s to give attention to guidelines. For instance, ‘hearken to’ sounds extra like ‘hear tuh’, with a schwa within the preposition ‘to’, fairly than ‘hearken to’ [/tuː/].
7. Are you able to share some closing phrases of knowledge on the subject of phrase stress in English?
I encourage my college students to make a recording of themselves copying what’s been mentioned after they’re listening to one thing. Ideally, the audio system needs to be proficient audio system of English. College students can then make a comparability of the 2 recordings, fascinated by phrase stress, sentence stress and intonation. These areas needs to be analysed one after the other.
After evaluating recordings, college students ought to attempt to regulate what they’ve mentioned so it matches the interlocutors’ speech. This isn’t about sounding a sure means or precisely the identical as a proficient speaker, be it a local speaker or not. Our accents are an integral a part of who we’re and we needs to be happy with them. The aim of constructing these voice recordings is to make speech extra intelligible.
A abstract of English phrase stress guidelines
On this part, I shall present an in-depth abstract of English phrase stress guidelines. I’ll spotlight the situations that affect which syllable is careworn in a phrase. To begin with, it appears acceptable to supply a basic introduction to phrase stress primarily based on a evaluate of the literature.
A Transient Overview of English Phrase Stress
To start this overview of English phrase stress guidelines, or tendencies, it appears acceptable to think about the construction of an English phrase. To begin with, English phrases consist of 1 syllable, two syllables, or many syllables. In all phrases of two or extra syllables, one syllable is extra outstanding, louder or extra noticeable than the opposite syllables in that phrase. Due to this fact, this robust syllable is careworn, or accented, whereas the opposite weaker syllables are unstressed, or unaccented:
- Careworn syllables – Careworn syllables sound louder, are usually longer, and have clearer vowels and stronger consonants. When a phrase is uttered in isolation, careworn syllables undertake a better pitch. In sentences, a pitch change (a shift in melody from excessive to low or low to excessive) typically happens on careworn syllables.
- Unstressed syllables – Unstressed syllables sound softer, are often shorter and are sometimes diminished. Which means that the vowels are inclined to undertake the qualities of schwa (/ə/) or diminished sounds equivalent to /ɪ/ and /ʊ/, whereas the consonants are weaker. The pitch doesn’t change route on unstressed syllables.
Stress will not be mounted to a selected syllable in English phrases, thus making English a free-stress language. Although stress can happen on first, second or third syllables and so forth, the location is nearly all the time mounted for particular person phrases, whatever the context. The phrase ‘perceived’, for instance, is all the time perCEIVED, by no means PERceived.
To spherical off this introduction to English phrase stress, it’s value highlighting a significant distinction between rhythm and phrase stress, as put ahead by Levin (2018, p.39):
… phrase stress sometimes is restricted to multi-syllabic phrases, whereas rhythm consists of stress for single-syllable phrases. In English, for instance, content material phrases (e.g., nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, negatives), together with these of 1 syllable, are usually careworn in discourse. Single-syllable perform phrases (e.g. prepositions, auxiliary verbs, pronouns, determiners) are sometimes unstressed in discourse.
The Significance of Phrase Stress in Communication
A plethora of authors (see, for instance: Fudge, 2016; Dauer, 1993 and Levis, 2018) have highlighted the significance of phrase stress in communication.
Fudge (2016, p.4) leads the best way in his evaluation of the seriousness of phrase stress. Based on Fudge (ibid.), a defective stressing will result in a “incorrect and deceptive rhythm” as a consequence of the truth that English rhythm is stress-timed. Rhythm fairly determines comprehensibility. Due to this fact, the putting of stress inside phrases can considerably impression how effectively a local English hearer will perceive the foreigner.
Dauer (1993, p.61) claims that stressing the right syllable in a phrase is equally necessary as announcing the sounds appropriately. That is significantly the case with heteronyms – phrases which have the identical spelling however totally different pronunciation. Two examples Dauer presents embrace:
1.
a. inlegitimate /ˈɪn.və.lɪd/ = a sick individual
b. invalid /ɪnˈvæl.ɪd/ = not legitimate or not appropriate
2.
a. console /ˈkɒn.səʊl/ = a floor or machine with controls for digital tools, a automobile, and many others
b. console /kənˈsəʊl/ = to make somebody really feel higher
Levis (2018, p.100) admits that misplaced phrase stress in English can halt communication solely:
When a phrase, particularly a phrase central to the understanding of the message, can’t be recognised, listeners could cease all different processing to decode the phrase that was not understood.
Oh what an environment
Levis (ibid.) describes a examine he ran on the ways in which educating assistants (TAs) remodeled a written textual content into spoken language. Basically, TAs had been supplied with a paragraph from a primary physics textual content on the sorts of power and the way they had been associated. They’d a brief period of time to organize their spoken presentation, which was video-recorded. A analysis assistant (RA) transcribed every presentation. In a single case, the RA couldn’t establish a phrase within the first sentence of a presentation from a speaker from India (“Effectively, we have now an excellent ____________ right now”).
Fortuitously, the researchers knew the subject and labored out the class of the phrase as a consequence of the truth that the sentence was in any other case grammatical. The most important challenge was that the speaker careworn the three-syllable phrase on the center syllable, which seemed like should or most. After a number of days of listening and making an attempt to decode the phrase, one of many researchers broke down the segmentals, arising with issues equivalent to ‘at most right here’. Finally, the researcher cracked the code with the phrase environment. Intelligibility arose as a result of this phrase is careworn on the center syllable in Indian English.
What are the primary acoustic alerts of careworn syllables?
The hearer perceives an accented syllable as extra outstanding than an unstressed syllable. Prominence is linked with the quantity of muscular power used to supply a syllable (Rogerson-Revell, 2011, p.138). The primary acoustic alerts of prominence are:
(1) Pitch change – If a syllable is alleged with a change in pitch, that’s both larger or decrease, the syllable will probably be extra outstanding to the hearer.
e.g. ba
ba ba ba(b) Syllable size – If one syllable in a phrase is longer than the others there’s a tendency to listen to it as careworn.
e.g. ba baa ba ba
Rogerson-Revell (ibid.) factors out that lengthy vowels (/i:/ /ɔ:/ /ɑ:/ /ɜ:/ /u:/) and diphthongs usually seem extra outstanding than shorter vowels. Nevertheless, lengthy vowels and diphthongs additionally crop up in unaccented syllables. Within the examples under, they aren’t careworn; nonetheless they nonetheless give an impression of prominence (the careworn syllable is marked with a ˈ).
phoneme / ˈfəʊni:m/
placard / ˈplækɑ:d/
railmeans / ˈreɪlweɪ/
tabletow / ˈpɪləʊ/
(c) Vowel high quality – An important facet of variations in vowel high quality is that unstressed syllables sometimes comprise a diminished vowel (both /ə/ or /i/ or /u/). Therefore, careworn syllables have a tendency to face out as a consequence of the truth that they’ve a full vowel.
e.g. bi
ba ba ba
(d) Syllable loudness – It is very important realise that it’s troublesome to extend loudness with out altering different qualities equivalent to pitch degree:
e.g. ba BA ba ba
Ranges of stress
Up to now, I’ve solely actually touched upon syllables by way of being both careworn or unstressed. In reality, syllables can have totally different levels of stress inside longer phrases. Due to this fact, when coping with phrases as they’re mentioned in isolation, we have to think about all syllables by way of their degree of stress.
There are commentators who’ve outlined extra levels of stress than might be essential on the subject of longer phrases. For example, Daniel Jones (1922, p.111) highlights the phrase alternative, which has 5 ranges of stress as seen under. ‘1’ signifies the best degree of stress, and ‘5’ the least:
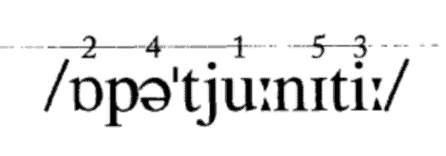
(In Kelly, 2000, p.69)
Relating to educating or learning phrase stress, Jones (1922, p.111) is fast to concede that “it’s usually enough to differentiate two levels [of stress] solely, careworn and unstressed.” Nevertheless, he goes on to say that it could generally be essential to differentiate three levels of stress. Based on Kelly (2000, p.69), commentators are inclined to decide on a three-level distinction between main stress, secondary stress and unstress for multi-syllable phrases, as is observable within the following examples:

(In Kelly, 2000, p.69)
When it comes to marking stress in written type, main stress is indicated by a excessive mark [ˈ]:
reˈturn /rɪˈtɜ:n/
Secondary stress could also be indicated by a low mark [ˌ] , as in:
ˌreveˈlation /ˌrevəˈleɪʃn/
conˌtamiˈnation /kənˌtæmɪnˈeɪʃn/
To spherical off this part, it’s value paying heed to Jones’s (1922, p.111) statement that, on the subject of multi-syllable phrases, “foreigners often put the secondary stress and even the first stress of the primary syllable”. That is the case with phrases equivalent to examination, peculiarity and administration, all of which comprise a secondary stress on the second syllable.
The position of stress inside an English phrase
Lastly, we have now come to the primary focus of this put up about English phrase stress guidelines. This query causes distinctive problem to English language learners:
How can one choose the right syllable or syllables to emphasize in an English phrase?
As Jennie and I touched upon within the interview, it’s not potential to pinpoint phrase stress within the English language merely in relation to the syllables of a phrase. As Roach (1991, p.88) places ahead:
Many writers have mentioned that English is so troublesome to foretell that it’s best to deal with stress placement as a property of the person phrase, to be realized when the phrase itself is realized.
Therefore, it’s laborious to disagree with Rogerson-Revell (2011, p.141) who states that: “Stress placement guidelines exist for English however they’re fairly advanced.” The English language learner is finest suggested to not suppose by way of English phrase stress guidelines however fairly basic tendencies for stress placement. Virtually the entire guidelines have exceptions.
Stress placement depends upon a wide range of components, together with:
- whether or not a phrase is morphologically easy (i.e. phrases consisting of a single morpheme), advanced (a phrase made up of two or extra morphemes and containing prefixes or suffixes) or a compound (two or extra phrases which were grouped collectively to create a brand new phrase that has a special, particular person which means, e.g. foot + ball = soccer).
- the grammatical class of a phrase (noun, verb, adjective, and many others.)
- the variety of syllables in a phrase
- the phonological construction of the syllables (e.g. closing syllables with quick vowels, one closing consonant, or a schwa sound (/ə/) aren’t careworn).
I’ll now spotlight these basic tendencies for stress placement in easy lexical phrases.
Two syllable phrases
a. Nouns
Most two syllable nouns (most notably correct nouns) have stress on the primary syllable:
e.g.
ˈPeter
ˈChristmas
ˈespresso
Nonetheless, if the second syllable is robust (i.e. it has a protracted vowel or a diphthong or ends in two consonants), then the second syllable is careworn.
e.g.
deˈsignal
eˈstate
Total, it’s uncommon for 2 syllable nouns to be careworn on the second syllable. It tends to be associated to borrowed phrases:
e.g.
laˈgoon
saˈloon
b. Verbs
Most two syllable verbs have stress on the second syllable, if that syllable is robust. Which means if the second syllable comprises a protracted vowel or diphthong, or it ends with a couple of consonant, that second syllable is careworn.
e.g.
apˈply
perˈsuade
reˈstrict
Conversely, if the ultimate syllable is weak (i.e. containing both a brief vowel or schwa and one, or no, closing consonant), then the primary syllable is careworn. A closing syllable can also be unstressed if it comprises /əʊ/, as in ‘borrow’ /ˈbɒrəʊ/.
e.g.
ˈenter
ˈenvy
ˈopen
After we think about these two-syllable verbs which can be exceptions to the above guidelines, the phrases could be perceived as being morphologically advanced (e.g. per‘mit).
c. Adjectives
Two syllable adjectives are inclined to comply with the identical sample as verbs.
e.g.
ˈlovely
corˈrect
aˈlive
ˈopen
English phrase stress guidelines aren’t set in stone. Due to this fact, there are fairly just a few exceptions to established tendencies on the subject of the stress placement in two-syllable adjectives.
e.g.
ˈhonest
ˈperfect
____
Lastly, different two-syllable phrases equivalent to prepositions and adverbs seem to behave like adjectives and verbs.
Phrase-class pairs
Mastering English phrase stress guidelines turns into even trickier when the foreigner begins to grapple with a bunch of phrases generally known as word-class pairs (homographs). Basically, these phrases function as each nouns and verbs and have equivalent spelling. They differ from one another by way of stress placement:
The mis-stressing of noun-verb pairs doesn’t appear to have an effect on intelligibility or comprehensibility for native listeners (Levis, 2018, p.116).
Three-syllable phrases
Relating to three-syllable phrases, there’s a tendency to place the stress in direction of the tip of the phrase on verbs and the entrance of the phrase for nouns.
a. Verbs
In verbs, if the ultimate syllable is powerful (with a protracted vowel, diphthong, or a couple of consonant), it is going to be careworn, as in:
enterˈtain beneathˈstand
In distinction, if the final syllable is weak (with a brief vowel and ends with not a couple of consonant), that syllable will probably be unstressed and the stress shifts ahead to the previous (penultimate) syllable, if that syllable is powerful, as in:
deˈvelop diˈrection
suˈrrender eˈxamine
b. Nouns
Relating to stress placement tendencies for three-syllable nouns, it’s helpful to seek the advice of Roach (1991, p.90).
To begin with, if the ultimate syllable comprises a brief vowel or /əʊ/, it’s unstressed. If the syllable which comes earlier than this closing syllable comprises a protracted vowel or diphthong, or if it ends with a couple of consonant, that center syllable will probably be careworn.
e.g.
potato /pəˈteɪ.təʊ/
catastrophe /dɪˈzɑː.stə/
Nonetheless, if the ultimate syllable comprises a brief vowel and the center syllable additionally comprises a brief vowel and ends with no more than a single consonant, these two syllables are unstressed. Stress placement ought to fall on the primary syllable:
e.g.
amount /ˈkwɒn.tə.ti/
cinema /ˈsɪn.ə.mə/
The aforementioned guidelines pertaining to nouns present stress tending to go on syllables which comprise a protracted vowel or diphthong and/or ending with a couple of consonant. Relating to three-syllable nouns, if the final syllable is of this sort, the primary syllable is often careworn. The final syllable tends to be outstanding which means that secondary stress comes into play.
e.g.
mind /ˈɪn·təlˌekt/
alkali /ˈæl·kəˌlɑɪ/
c. Adjectives
Many adjectives are inclined to comply with the instantly previous rule pertaining to nouns. The primary syllable tends to be careworn whereas the final syllable often adopts secondary stress:
e.g.
derelict /ˈder·əˌlɪkt/
Stress in advanced phrases
To date, we have now thought-about English phrase stress guidelines regarding ‘easy’ phrases, particularly phrases comprising a single grammatical unit. Nevertheless, there are many phrases which include a couple of grammatical half. For example, ‘hope’ + ‘much less’ = ‘hopeless’ and ‘idiot’ + ‘ish’ = ‘silly’. Such advanced phrases fall into two classes:
(a) Phrases constructed from a primary stem along with an affix (i.e. a prefix equivalent to ‘un’ + nice = disagreeable, or a suffix equivalent to ‘ready’ + go well with = appropriate
(b) compound phrases (e.g. ice-cream, armchair)
(a) Phrases with affixes (prefixes and suffixes)
Affixes can have an effect on phrase stress in 3 ways:
(i) the affix is careworn – e.g. ˌJapaˈnese
(ii) the affix has no impact – e.g. ˈmarket – ˈadvertising
(iii) the affix will not be careworn however the stress on the stem shifts – e.g. ˈmagnet – magazineˈnetic
(i) The affix is careworn = ‘Autostressed’ Suffixes
There are circumstances when the first stress falls on the suffix (e.g. entrepreˈneur) or strikes onto a suffix, as in:
Jaˈpan – ˌJapaˈnese
ˈmountain –ˌmountainˈeer
Phrases containing greater than two syllables may even see their root buying a secondary stress, as within the examples above.
Single-syllable prefixes don’t often carry stress (e.g. misˈdecide). Nevertheless, longer prefixes could carry secondary stress (e.g. ˌantiˈclockwise).
Fudge (2016, p.41) offers an entire record of autostressed suffixes. Amongst them are:
- ade
- aire
- ee
- een
- esce
- esque
- ette
- eur
- oon
- teen
(ii) Suffixes that don’t have an effect on stress placement
There are a lot of circumstances during which the suffix doesn’t have an effect on stress placement. For example:
-able – beneathˈstand – beneathˈstandable; ˈconsolation – ˈsnug
-age – ˈcowl – ˈprotection, ˈbag –ˈbaggage
-al – ecoˈnomic – ecoˈnomical; geoˈgraphic – geoˈgraphical
-ful – ˈcare – ˈcautious; ˈwonder- ˈfantastic
(iii) Suffixes that affect stress within the stem
Right here, the suffix causes the stress on the phrase stem to maneuver. For instance:
-eous – advertˈvantage; advanˈtageous
-ic – eˈconomy, ecoˈnomic; ˈtechnique, straˈtegic
Additional studying on suffixes
Fudge (2016, p.52-103) devotes over 50 pages of his e book to a complete record of suffixes with their properties. Such in depth protection proves why the scholar of English mustn’t get slowed down with English phrase stress guidelines as a result of they’re seemingly infinite in quantity.
Prefixes
Roach (1991, p.98) offers with the subject prefixes very succinctly. He states that the impact of prefixes on stress doesn’t have the “comparative regularity, independence and predictability of suffixes”. Furthermore, there is no such thing as a prefix of both one or two syllables which all the time carries main stress. Due to this fact, Roach (ibid.) concludes that “stress in phrases with prefixes is ruled by the identical guidelines as these for phrases with out prefixes”.
(b) Stress in compound phrases
In Fudge’s (2016, p.34) eyes compound phrases are distinctive in that they’re:
… mixtures of phrases which will happen independently elsewhere, and therefore have to be two phrases; on the identical time, they’re mixed in such a means that they type a single comparatively close-knit complete with numerous traits that point out fairly clearly that they’re one phrase.
Fudge (ibid.) goes on to say that compounds possess most of the accentual and rhythmic traits of single phrases. Due to this fact, they have an inclination to have a most important stress close to the starting of the mixture. Equally, single phrases are inclined to bear penultimate or antepenultimate stress fairly than closing stress. In distinction, phrase constructions, which afford the person phrases rather more independence, usually have most important stress on their closing factor.
Fudge (2016, p.34) illuminates the distinction between compounds and phrase constructions by means of the examples of blackboard and black board. The compound noun blackboard (i.e. a board for writing on with chalk) takes main stress on the primary factor black. As for the noun phrase black board, it usually has nuclear stress on the second factor board.
Compound phrases could also be written in a wide range of methods:
(a) as one phrase – e.g. ‘sunflower’, ‘typewriter’ and ‘doorbell’
(b) with the phrases separated by a hyphen – e.g. ‘car-ferry’ and ‘fruit-cake’
(c) with two phrases separated by an area – e.g. ‘battery charger’ and ‘desk lamp’
Compounds which mix two nouns
As beforehand alluded to with the compound noun blackboard, compounds which comprise two nouns and performance as nouns, usually put the stress on the primary noun:
e.g.
ˈtypewriter
ˈgreenhouse
ˈsuitcase
Compounds which perform as adjectives, verbs or adverbs
Compounds which perform as adjectives (with the -ed morpheme on the finish), verbs or adverbs, generally put the stress on the second factor:
e.g.
bad-ˈtempered (unhealthy = adjectival)
ill-ˈdeal with (compound which capabilities as a verb with an adverbial first factor)
North-ˈEast (compound functioning as an adverb)
Issues with English Phrase Stress Guidelines
On numerous events, this put up has highlighted the truth that English phrase stress guidelines are awash with inconsistencies, shocking twists and exceptions. It will be truthful to exchange the phrase ‘guidelines’ with ‘tendencies’.
Levis (2018, p.102) sums up the scenario very aptly certainly:
Accounting for English phrase stress requires a hodgepodge of various patterns associated to the size of the phrase, its lexical class, etymological origin, kinds of affixation, when the phrase grew to become a part of English.
Levis (2018, p.256) additionally concedes that English phrase stress is a closely under-researched class of examine:
… there’s a lot that we have no idea about phrase stress and its position in intelligibility. For instance, we have no idea precisely what word-stress issues are widespread for learners of assorted proficiency ranges, which word-stress issues have an effect on understanding for NS and/or NNS listeners, whether or not learners can understand stress however not produce it, or vice versa.
Among the most critical points associated to English phrase stress embrace:
1. Interference from the learner’s L1
There are numerous points associated to the learner’s L1 which regularly forestall the manufacturing of appropriate phrase stress in English. Rogerson-Revell (2011, pp.151-52) lists a few of the causes learners ceaselessly have difficulties with phrase stress as a consequence of interference from their L1, together with:
(i) There could also be a propensity to provide each careworn and unstressed syllables full vowels (i.e. vowels in unstressed syllables aren’t weakened), as for example within the Italian and French languages.
(ii) Phrase stress could also be mounted within the L1 (i.e. stress tends to fall on a selected syllable). For instance, the ultimate syllable in French and Thai and the penultimate syllable in Swahili and Polish.
(iii) The L1 could have variable fairly than mounted stress placement (as in English) however totally different guidelines, as in Turkish, Italian and Arabic. This may occasionally result in explicit issues with cognates.
(iv) The L1 could solely have main stress, as in Russian and Greek. This may occasionally trigger issues with multisyllabic phrases.
(v) In lots of languages there is no such thing as a compound phrase stress distinction, for instance, white ‘home’ vs ‘White Home’. The distinction is fairly signalled by phrase order versus phrase stress.
(vi) Compound phrase stress could all the time be on the primary syllable (e.g. ‘prime minister’, ‘entrance door’), as in German and Scandinavian languages.
(vii) ‘Worldwide’ phrases, particularly cognates equivalent to ‘tv’, are topic to interference from the learner’s L1. ‘Tv’ doesn’t have penultimate stress and has 5 fairly than 4 syllables in lots of languages.
2. Phrase stress is usually studied/taught artificially as phrases are usually analysed as they’re mentioned in isolation
English phrase stress guidelines relate to phrases as they’re mentioned in isolation. Actually, as Roach (1991, p.95) factors out, learning phrases in isolation does reveal stress placement and stress ranges extra clearly than analysing them within the context of fast, steady speech. Nonetheless, it’s nonetheless a considerably synthetic scenario to give attention to the stress of remoted phrases. In any case, we not often say phrases in isolation, aside from, for example, ‘presumably’, ‘sure’, please’ and interrogative phrases equivalent to ‘what’.
As one begins to analyse how phrase stress varies relying on the place of a phrase in a sentence, then it turns into simpler to understand why it’s typically a fruitless process to review the stress of phrases as they’re mentioned insolation.
Dauer (1993, p.105), for example, appears at how the stress in some phrases and compounds careworn on the final syllable could shift place relying on their location in a sentence. Basically, phrases are careworn on the final syllable (or final “phrase”) when it happens on the finish of a sentence or phrase. In distinction, one ought to stress the first syllable (or first “phrase”) when it’s instantly succeeded by one other phrase in the identical phrase. That is typically the case when the phrase capabilities as an adjective and is adopted by a noun that’s careworn on the primary syllable. Dauer (ibid.) presents the next sentences as a way to stress phrases with variable stress:

in Dauer, 1993, p.105
3. Bewildering problems and exceptions plague most areas of phrase stress in English
I’d certainly want one other 25,000 phrases to cowl all of the exceptions to, and problems of, what look like even probably the most steady of English phrase stress guidelines.
Nevertheless, to light up the difficulties each learners and academics face on the subject of tackling English phrase stress, we must always return to the subject of stress in compounds. On the face of it, there’s a clear-cut distinction between phrases (taking closing stress, e.g. black ˈboard) and compounds (taking preliminary stress, ˈblackˌboard). Nevertheless, as Fudge (2016, p.136) questions, what about constructions that are syntactically much like compounds but they take phrasal stress patterns? Fudge (ibid.) compares ˈChristmas ˌcake (with the common compound stress-pattern), and Christmas ˈpudding and Christmas ˈpie (with the phrasal sort of sample and stress on the second phrase).
With the aforementioned examples of Christmas meals in thoughts, it’s obvious that there are only a few English phrase stress guidelines which can be of a hard-and-fast nature. Fudge (2017, pp.144-49) presents 22 most important regularities associated to the task of preliminary or closing stress to compounds. Unsurprisingly, a terrific many of those regularities comprise exceptions. This means that learners ought to give attention to noticing stress patterns of particular person phrases and compounds and many others. after they interact in listening observe fairly than consciously purpose to ‘be taught’ or memorise English phrase stress guidelines.
Phrase stress train with solutions and audio information
Jennie kindly shared an train associated to phrase stress. Obtain the train, which additionally comprises solutions, in PDF type utilizing the hyperlink under. Do additionally obtain the audio information.
Ultimate Ideas on Phrase Stress Guidelines
This put up has established that academics of English face a real quandary on the subject of educating English phrase stress guidelines. On condition that these guidelines, or tendencies, are topic to a terrific many exceptions, one actually has to think about whether or not it’s value dedicating vital instruction time particularly to phrase stress.
Nonetheless, I imagine that academics mustn’t utterly overlook phrase stress. As for academics who do have information of the phonology of the scholar’s first language, then they’re in a robust place to at the least draw consideration to why unfavourable language switch from the scholar’s mom tongue could also be stopping the manufacturing of appropriate phrase stress in English. All in all, I believe it’s a case of instructing and drip-feeding info to college students when critical situations of intelligibility do happen and when the time is in any other case proper.
References
Dauer, R.M., (2005). The Lingua Franca Core: A New Mannequin for Pronunciation Instruction? TESOL Quarterly, Vol. 39, No. 3 (Sep., 2005), pp. 543-550
Dauer, R.M., (1993). Correct English: A Full Course in Pronunciation, Prentice Corridor Regents: USA
Fudge, E., (2016). English Phrase-Stress, Abingdon: Routledge
Jones, D., (1922). An Define of English Phonetics, New York: G.E. Stechert & Co.
Kelly, G., (2000). Easy methods to Educate Pronunciation, Harlow: Pearson Training Restricted
Levis, J.M., (2018). Intelligibility, Oral Communication, and the Educating of Pronunciation, Cambridge: Cambridge College Press
Roach, P., (1991). English Phonetics and Phonology: A sensible course, Second version, Cambridge: Cambridge College Press
Rogerson-Revell, P., (2011). English Phonology and Pronunciation Educating, New York: Continuum Worldwide Publishing Group
Underhill, A., (2005). Sound Foundations: Studying and educating pronunciation, Oxford: Macmillan Training